[ad_1]
A group of Neanderthal tools made between 120,000 and 40,000 years ago were prepared with glue, according to a team of researchers who recently studied the objects.
Research has revealed the oldest evidence of a complex adhesive substance in Europe, according to a NYU release, The adhesive – composed of bitumen, an asphalt component also found naturally in clay, and ocher – was found in small quantities on stone tools from the Neanderthal site of Le Moustier in France. the conclusions were published This week in Science Advances.
“When used as handheld grips on cutting or scraping tools, high-ocher adhesives offer a real advantage, improving their tenacity and toughness,” the authors write in the paper. ‘
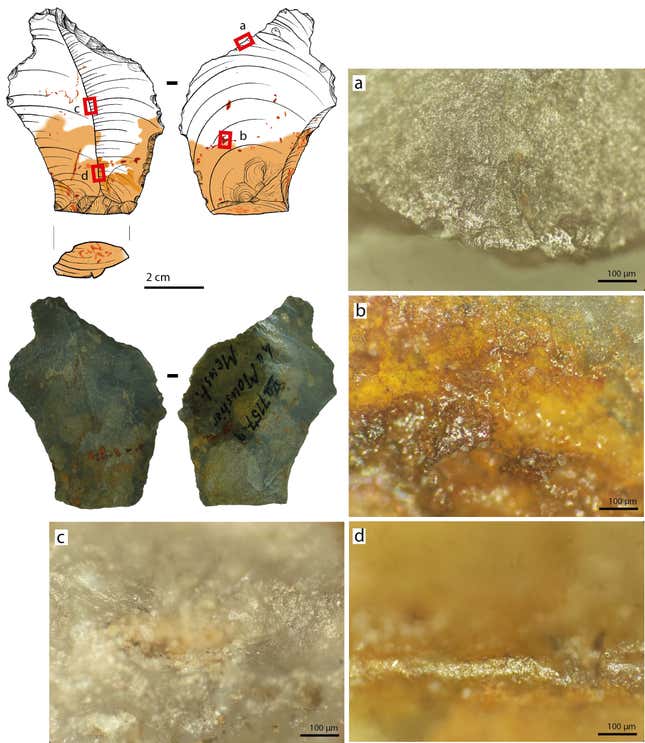
Bitumen itself is an adhesive, but as a liquid it does not make a great glue. But when it is mixed with ocher the same thing happens Neanderthals and early modern humans used This creates a sculptural solid, which Neanderthals applied to scrapers, flakes and blades at Le Moustier – to create artwork on cave walls. The team studied five stone tools that had traces of ocher: three fragments, a retouched blade, and a side scraper.
“Compound adhesion is thought to be one of the first manifestations of modern cognitive processes that are still active today,” Patrick Schmidt, an archaeologist at the University of Tübingen and lead author of the study, said in the same release. Neanderthals were intelligent and inventive, as evidenced by their artefacts and array of tool,
The glued-together bitumen-ochre mass stuck well to the stone, but did not stick to the hands – making it an ideal material for crafting tool handles. Microscopic imaging of the devices revealed two types of wear: one that indicated that other materials had been worked on and one that indicated that the adhesive itself had deteriorated due to use. Again, the team believes that adhesive substances were used to attach stone tools to the handles rather than the handles themselves.
Le Moustier was discovered in 1907 but has been in storage since the 1960s. “As a result, the chipped remains of organic material were very well preserved,” Ewa Dutkiewicz, co-author of the study and a researcher at the University of Tübingen and the Museum of Prehistory and Early History of Berlin, said in the release.
Our Modern understanding of Neanderthals is far from old, obsolete ideas about our nearest Homosexual Relative. Although they became extinct about 40,000 years ago, Neanderthal DNA persists In most people today, it is an indicator of how Neanderthals gradually assimilated into In a wise man,
[ad_2]

